
If you have gout, chances are your doctor has prescribed urate-lowering therapy (ULT) to reduce the amount of uric acid in your bloodstream and help manage the disease.1 But did you know that you might also need to take an anti-inflammatory medicine such as Colchicine to prevent gout flares?1 Read on to find out more about why taking Colchicine (or another anti-inflammatory drug) is important if you’re on ULT.1
The role of ULT in gout management
The goals of long-term gout therapy are to1:
- Reduce the amount of uric acid in the bloodstream
- Reduce the number of occurrences of acute gout flares
- Reduce the appearance of tophi (deposits of uric acid crystals around the joints that are visible through the skin)
- Prevent joint damage
To reap these benefits, most patients need to start ULT and stay on it until their uric acid approaches normal levels (<6.0 mg/dL).1
Taking Colchicine with ULT is important
If you have gout, your doctor may have prescribed a ULT to help reduce the amount of uric acid in your bloodstream. However, this reduction in the uric acid level can disturb the uric acid crystals in a joint, and this disturbance can trigger a gout flare.1 Taking a colchicine product such as Mitigare® (Colchicine) 0.6 mg Capsules with ULT can help prevent these painful flares.2
Start Colchicine as soon as ULT begins
If you’re not having flares, you may be more likely to stay on ULT and successfully achieve your target uric acid goals.1 Colchicine therapy is clinically proven to reduce the frequency of flares in people with gout.3
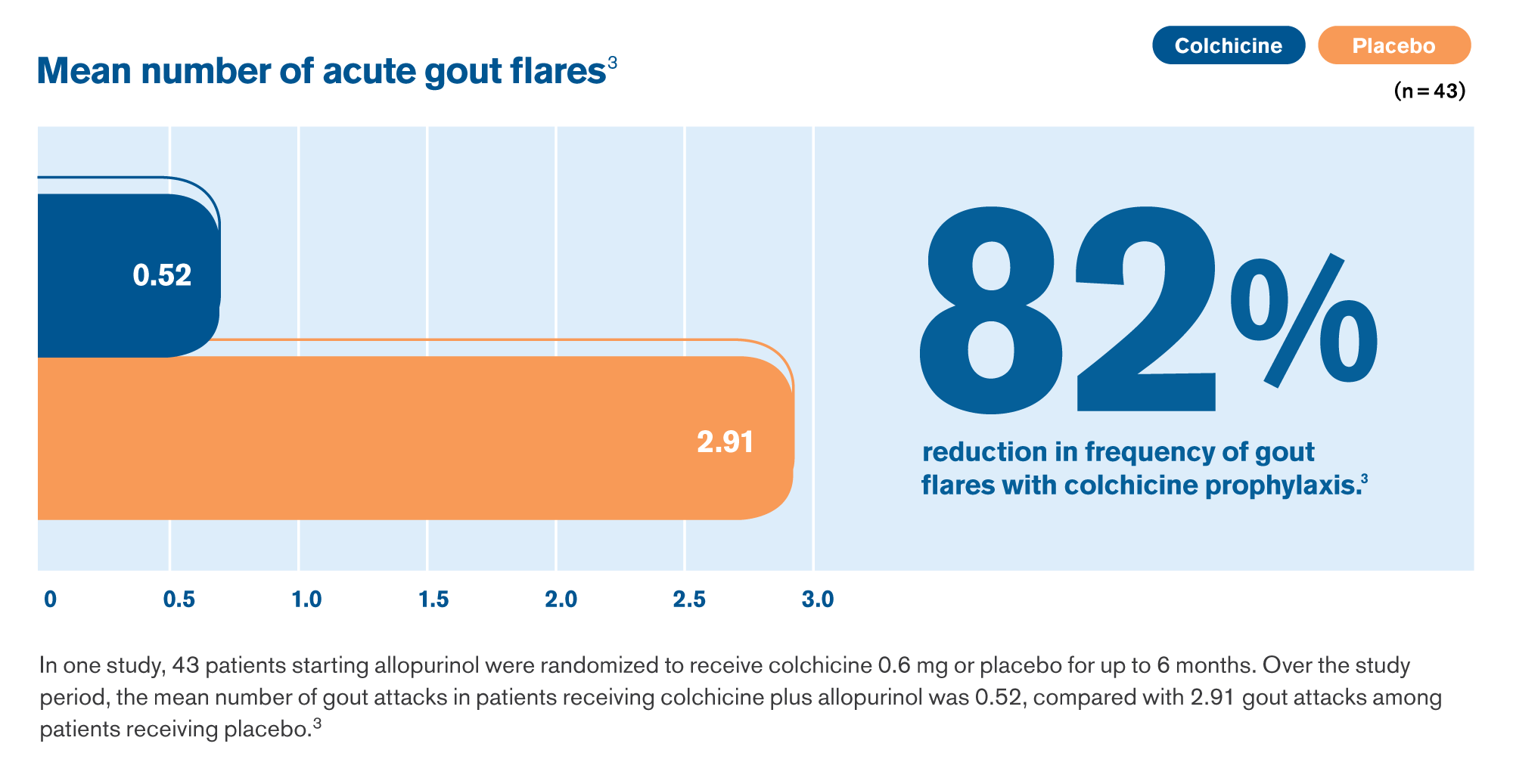
The new standard of care for taking Colchicine with ULT
The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) gout management guidelines strongly recommend that people who are taking ULT also take an anti-inflammatory medication such as to help prevent gout attacks. In fact, the ACR gout management guidelines—2019 draft, due out after peer review later this year, recommended that people on ULT take an anti-inflammatory medication for at least three to six months*—significantly longer than the original recommendation of three months or less.
Talk with your doctor about taking Colchicine with ULT
If you are taking ULT and still suffer with gout flares, talk with your doctor. He or she can write you a prescription for Mitigare® (Colchicine) 0.6 mg Capsules or Generic Colchicine Capsules. Your doctor may even be able to help you save money on Colchicine therapy through the Mitigare® True Blue Savings program.
*With ongoing evaluation and continued prophylaxis as needed if the patient continues to experience flares.
Mitigare® is a registered trademark of Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc.
Colchicine 0.6 mg capsules are contraindicated in patients with renal or hepatic impairment who are currently prescribed drugs that inhibit both P-gp and CYP3A4. Combining these dual inhibitors with colchicine in patients with renal or hepatic impairment has resulted in life-threatening or fatal colchicine toxicity. Patients with both renal and hepatic impairment should not be given Mitigare®.
Fatal overdoses have been reported with colchicine in adults and children. Keep Mitigare® out of the reach of children.
Blood dyscrasias such as myelosuppression, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia and aplastic anemia have been reported with colchicine used in therapeutic doses.
Monitor for toxicity and, if present, consider temporary interruption or discontinuation of colchicine.
Drug interaction with dual P-gp and CYP3A4 inhibitors: Co-administration of colchicine with dual P-gp and CYP3A4 inhibitors has resulted in life-threatening interactions and death.
Neuromuscular toxicity and rhabdomyolysis may occur with chronic treatment with colchicine in therapeutic doses, especially in combination with other drugs known to cause this effect. Patients with impaired renal function and elderly patients (including those with normal renal and hepatic function) are at increased risk. Consider temporary interruption or discontinuation of Mitigare®.
The most commonly reported adverse reactions with colchicine are gastrointestinal symptoms, including diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain.
Please see the full Prescribing Information and Medication Guide for Mitigare® for complete product details.
NOTE: This article was not written by a medical professional and is not intended to substitute for the guidance of a physician. These are not Hikma’s recommendations for gout flare prevention, but rather facts and data collected from various reliable medical sources. For a full list of resources and their attributing links, see below.
